- Control Valve
- Pneumatic Control Valve
- Pneumatic Angle Control Valve
- 3 Way pneumatic Diaphragm Control Valve
- 3 Way Converging and Diverging Control Valve
- Fluorine Lined Single Seat Control Valve
- Pneumatic Cage Control Valve
- Pneumatic Double Seat Control Valve
- Pneumatic Single Seat Globe Control Valve
- Pneumatic Flow Control Valve
- Pneumatic Sleeve Type Control Valve
- Pneumatic Actuated Globe Type Control Valve
- Electric Actuated Control Valve
- Pneumatic Control Valve
- Cryogenic Valve
- Pressure Reducing Valve
- Safety Valve
- Check Valve
- Gate Valve
- Butterfly Valve
- Globe Valve
- Ball Valve
- Electric Actuated Valve
- Electric Actuated Ball Valve
- Electric Actuated Butterfly Valve
- Electric Actuated Gate Valve
- Electric Actuated Globe Valve
- Pneumatic Actuated Valve
- Plunger Valve
- Strainers
- Steam Trap
- Knife Gate Valve
- Speciality Valve
- Alloy 20 Valve
- Duplex Valve
- Super Duplex Valve
- Hastelloy C276/B3 Valve
- Aluminium Bronze Valve
- Titanium Valve
- Bronze Valve
- Monel Valve
- Triple Duty Valve
- Suction Diffuser
- Diaphragm Valve
- Plug Valve
- Foot Valve
- Air Release Valve
- Surge Anticipator Valve
- Needle Valve
- Balancing Valve
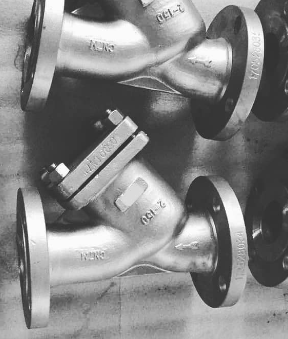
Y Strainer
Middleeast valve is well known for Y strainer manufacturers in Saudi Arabia. A Y strainer, also known as a Y filter, is an essential device used in various fluid-handling applications to remove unwanted solid particles from liquid, gas, or steam systems. The device is named after its Y-shaped configuration, which features a main pipeline and an angled branch that houses a mesh or perforated straining element.
Y strainers are integral to maintaining system efficiency and protecting downstream equipment from potential damage caused by contaminants.
Y strainers operate based on a simple yet effective principle: as fluid flows through the strainer, it passes through the straining element (mesh or perforated screen). The straining element traps debris and solid particles, allowing the cleaned fluid to continue through the pipeline. The trapped debris can then be removed by cleaning or replacing the straining element as part of regular maintenance.
The straining process can be broken down into the following steps:
Fluid Entry: Fluid enters the strainer body through the inlet.
Filtration: The fluid flows through the straining element, which captures solid particles.
Debris Collection: Captured debris collects in the strainer element, while clean fluid exits through the outlet.
Maintenance: The strainer element is periodically cleaned or replaced to ensure optimal performance.
Y strainers serve several critical functions in fluid-handling systems:
Protection of Equipment: By removing solid particles from the fluid, Y strainers protect downstream equipment such as pumps, valves, and heat exchangers from damage and wear.
Improving System Efficiency: Clean fluids help maintain optimal performance and efficiency of the system, reducing the risk of clogging and pressure drops.
Extending Equipment Life: Regular filtration reduces the risk of abrasion and corrosion, extending the lifespan of critical components.
Ensuring Product Quality: In processes where fluid purity is essential, Y strainers help maintain the required quality standards by removing contaminants.
Reducing Maintenance Costs: By preventing the accumulation of debris in the system, Y strainers reduce the frequency and cost of maintenance and repairs.
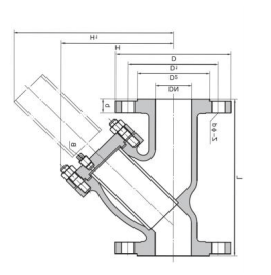
Description:
Body: Carbon Steel, CF8, CF8M, CF3M, Cast Iron, SS304, SS316, SS304, SS304L, SS316, SS316L
Class: 150-2500
Nominal Pressure: PN6- PN450
Size: ½” to 24”
Ends: Buttweld, Flanged, Socket weld, Threaded.