- Control Valve
- Pneumatic Control Valve
- Pneumatic Angle Control Valve
- 3 Way pneumatic Diaphragm Control Valve
- 3 Way Converging and Diverging Control Valve
- Fluorine Lined Single Seat Control Valve
- Pneumatic Cage Control Valve
- Pneumatic Double Seat Control Valve
- Pneumatic Single Seat Globe Control Valve
- Pneumatic Flow Control Valve
- Pneumatic Sleeve Type Control Valve
- Pneumatic Actuated Globe Type Control Valve
- Electric Actuated Control Valve
- Pneumatic Control Valve
- Cryogenic Valve
- Pressure Reducing Valve
- Safety Valve
- Check Valve
- Gate Valve
- Butterfly Valve
- Globe Valve
- Ball Valve
- Electric Actuated Valve
- Electric Actuated Ball Valve
- Electric Actuated Butterfly Valve
- Electric Actuated Gate Valve
- Electric Actuated Globe Valve
- Pneumatic Actuated Valve
- Plunger Valve
- Strainers
- Steam Trap
- Knife Gate Valve
- Speciality Valve
- Alloy 20 Valve
- Duplex Valve
- Super Duplex Valve
- Hastelloy C276/B3 Valve
- Aluminium Bronze Valve
- Titanium Valve
- Bronze Valve
- Monel Valve
- Triple Duty Valve
- Suction Diffuser
- Diaphragm Valve
- Plug Valve
- Foot Valve
- Air Release Valve
- Surge Anticipator Valve
- Needle Valve
- Balancing Valve
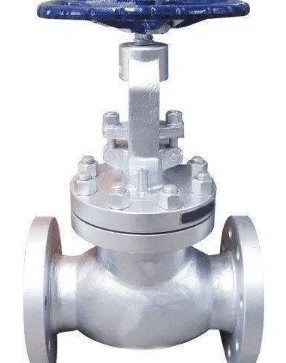
A titanium globe valve is a type of valve used to control the flow of liquids and gases in a pipeline. Made from titanium, a material known for its exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and light weight, this valve is ideal for applications where high durability and resistance to corrosive environments are required. Titanium globe valves are commonly used in industries such as chemical processing, oil and gas, and marine engineering.
Function of a Titanium Globe Valve
The primary function of a titanium globe valve is to regulate, start, or stop the flow of a fluid within a pipeline. It provides precise throttling control, making it suitable for applications where accurate flow regulation is necessary. Its unique design allows it to handle high pressure and temperature, making it an excellent choice for challenging industrial environments.
How Does a Titanium Globe Valve Work?
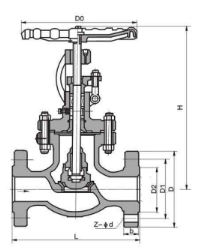
A titanium globe valve consists of a movable disk (or plug) and a stationary ring seat. The disk is connected to a stem, which is controlled by a handwheel or actuator. When the valve is open, the disk is lifted away from the seat, allowing fluid to pass through. As the valve is closed, the disk moves towards the seat, reducing the flow until it is fully shut off. The linear motion of the stem ensures precise control over the flow rate, which is particularly useful for throttling applications.
The titanium material of the valve body provides a high level of resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for use in harsh environments where other materials might fail.
Key Features of Titanium Globe Valves:
1)Corrosion Resistance: Titanium offers excellent resistance to corrosion from seawater, acids, alkalis, and other aggressive chemicals, making these valves suitable for use in highly corrosive environments.
2)High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Titanium globe valves are lightweight yet extremely strong, which makes them easy to handle and install without compromising on durability or performance.
3)Precise Flow Control: The design of the globe valve, with its linear motion and tight shut-off capability, provides precise flow control, ideal for applications requiring exact regulation of fluids.
4)Temperature and Pressure Resilience: Titanium globe valves can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for various demanding industrial applications.
5)Durability: Due to the robust properties of titanium, these valves have a longer service life and require less maintenance compared to valves made from other materials.
6)Low Maintenance: The corrosion-resistant nature of titanium reduces the need for frequent repairs and maintenance, leading to lower operational costs over time.
Applications of Titanium Globe Valves:
1)Chemical Processing: For handling corrosive chemicals and high-temperature fluids.
2)Oil and Gas: Used in offshore and onshore operations, especially in harsh environments.
3)Marine Industry: Ideal for seawater applications due to their resistance to corrosion.
4)Power Generation: For regulating steam and other fluids in high-temperature environments.