- Control Valve
- Pneumatic Control Valve
- Pneumatic Angle Control Valve
- 3 Way pneumatic Diaphragm Control Valve
- 3 Way Converging and Diverging Control Valve
- Fluorine Lined Single Seat Control Valve
- Pneumatic Cage Control Valve
- Pneumatic Double Seat Control Valve
- Pneumatic Single Seat Globe Control Valve
- Pneumatic Flow Control Valve
- Pneumatic Sleeve Type Control Valve
- Pneumatic Actuated Globe Type Control Valve
- Electric Actuated Control Valve
- Pneumatic Control Valve
- Cryogenic Valve
- Pressure Reducing Valve
- Safety Valve
- Check Valve
- Gate Valve
- Butterfly Valve
- Globe Valve
- Ball Valve
- Electric Actuated Valve
- Electric Actuated Ball Valve
- Electric Actuated Butterfly Valve
- Electric Actuated Gate Valve
- Electric Actuated Globe Valve
- Pneumatic Actuated Valve
- Plunger Valve
- Strainers
- Steam Trap
- Knife Gate Valve
- Speciality Valve
- Alloy 20 Valve
- Duplex Valve
- Super Duplex Valve
- Hastelloy C276/B3 Valve
- Aluminium Bronze Valve
- Titanium Valve
- Bronze Valve
- Monel Valve
- Triple Duty Valve
- Suction Diffuser
- Diaphragm Valve
- Plug Valve
- Foot Valve
- Air Release Valve
- Surge Anticipator Valve
- Needle Valve
- Balancing Valve
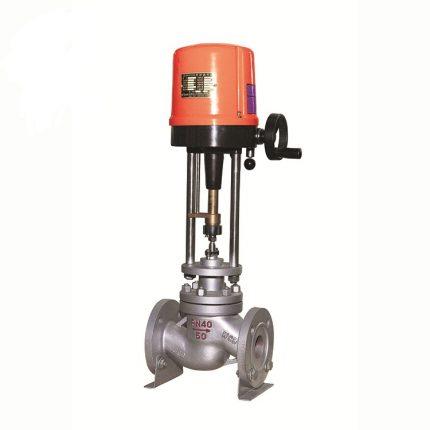
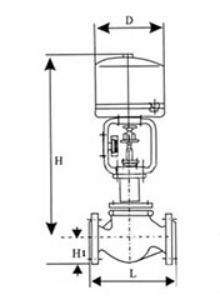
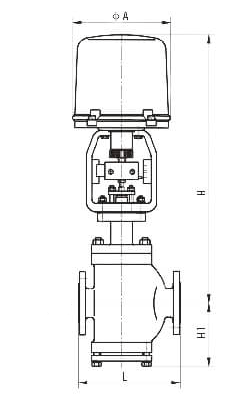
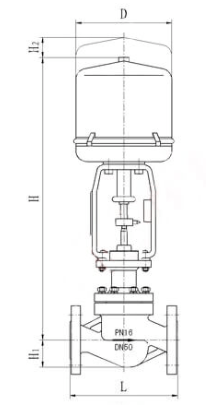
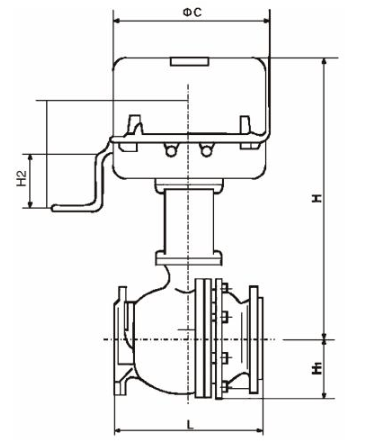
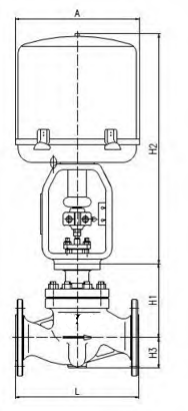
Electric Actuated Control Valve Supplier in Saudi Arabia: Automation for Optimal Performance
Middleeast valve is the leading Electric Actuated Control Valve Supplier in Riyadh. An Electric Actuated Control Valve is a type of valve that uses an electric actuator to control the flow of fluids (liquids, gases, or slurries) within a system. The actuator, powered by electricity, moves the valve’s components (like the plug, ball, or disk) to regulate the flow according to the process requirements. These valves are commonly used in industries such as water treatment, oil and gas, chemical processing, and HVAC systems for precise and automated flow control.
Key Parts:
1)Electric Actuator: The electric motor that drives the valve mechanism to open or close in response to control signals.
2)Valve Body: The principal housing which carries all internal valve components.
3)Control Signals: Electrical signals being sent from controllers to the actuator and cause the valve to change its position.
4)Positioner: Responsible for making the valve reach a desired position for precise control.
5)Stem and Plug: The mechanical components which alter the valve opening to manage flow.
Working Mechanism:
The electric actuator is activated by an electrical control signal which move valve to desired position. As soon as the actuator is signaled, it moves the stem or plug to control fluid flow. The valve constantly holds the right flow, pressure, or temperature by adapting to the control signals, giving an accurate and automated industrial process solution.
Advantages:
1)Accurate Control: Electric actuated control valves provide accurate and consistent control.
2)Energy Efficiency: These valves use very little energy as opposed to other actuators.
3)Low Maintenance: Electric actuators are low maintenance, providing long-term reliability.
4)Automated Operations: Ideal for systems that need automation, minimizing human intervention.
Industries:
1)Oil and gas
2)Water treatment
3)HVAC
Description:
Available Materials: Ductile Iron, Cast iron(WCB, WCC, WC6) LCC, LCB, Stainless Steel (SS316, SS304), Super Duplex (F51, F53, F55)
Class: 150 to 2500
Size: 1/2”- 24”
Ends: Flanged, butt weld, socket weld, threaded
Operations: Electric actuated and Pneumatic actuated
Electric Actuator:
1)Torque: 3-9 Nm
2)Operating Pressure: 8 Bar
3)Port Connection: NPT 1/4″
4)Mounting Base: ISO 5211
5)Temperature Range: -20°C to +80°C
Pneumatic Actuator Configuration:
1)4-20 mA
2)Single Acting
3)Double Acting
4)Rotary
5)Scotch and Yoke
6)Pressure: Up to 228 bar
Temperature Ranges:
1)Standard: -4°F to 200°F (-20°C to 93°C)
2)Low: -40°F to 176°F (-40°C to 80°C)
3)High: 0°F to 300°F (-18°C to 149°C)